Monday-Friday 6:00am – 5:00pm | Saturday 6:00am – 12:00pm

Urine Drug Testing+
Reduce risks and avoid costs associated with drug abuse

Advanced Urine Drug Testing
12 Panel
10 Panel
6 Panel
5 Panel
3 Panel
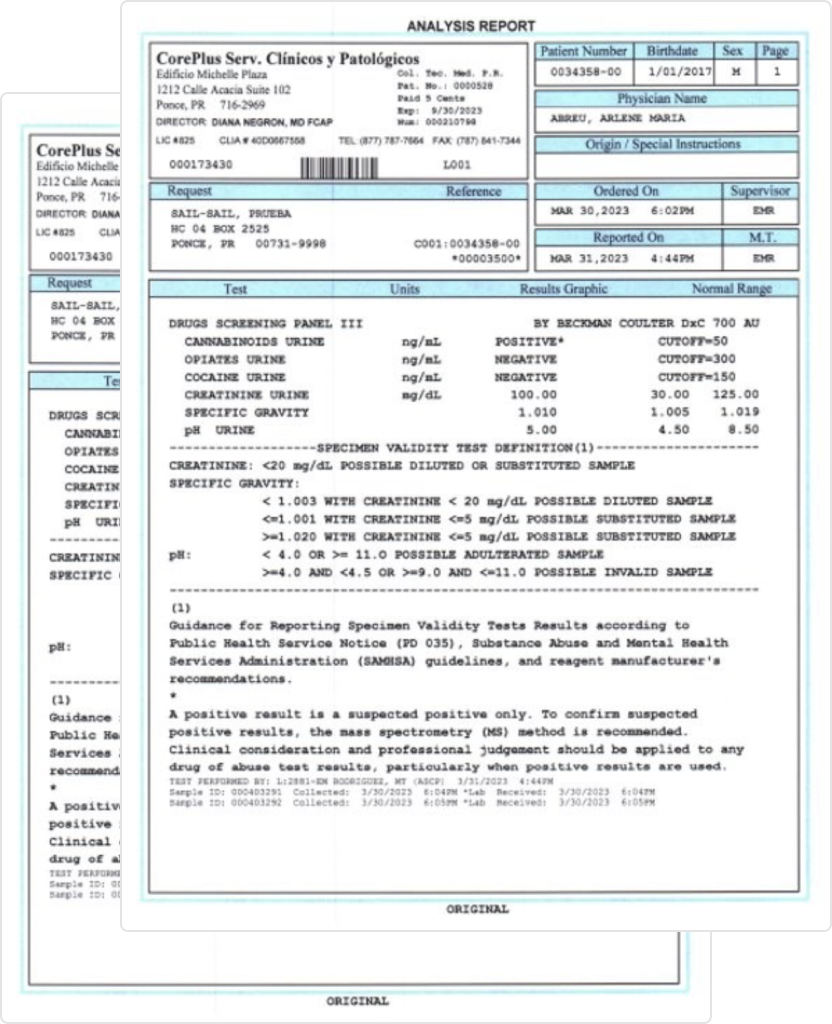
Specimen Validity Testing
Urine Drug Testing+ Test Menu
Cocaine, Amphetamines, Opiates, PCP, Methadone, Benzodiazepines, Heroin, Barbiturates, Methamphetamines, THC, Buprenorphine, Oxycodone
+Specimen Validity (pH, Specific Gravity, Creatinine) Included
*Narcotic Only panels (No THC test option)
Urine Specimens 101 – While it is the most common drug testing method, Urine testing is not foolproof. Common Alterations of Urine include Adulterated specimen, Diluted specimen, Substituted specimens. Often not detectable by POC cups
UDT+ Includes Specimen Validity Testing. With specimen validity testing, we can help ensure the integrity of the test by measuring pH, creatinine and specific gravity.
CorePlus Advanced Solution
Pros vs. Cons

Disadvantages of POCT testing include:

Advantages of Lab Based Testing:
Pharmacology+ testing:
Clinical Toxicology
Educational Content & Related Links
Urine Drug Testing Fact SheetNational Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)American Chronic Pain AssociationGuidelines for the Chronic Use of OpioidPain Management Drug Testing Is on the RiseClinical Drug Testing in Primary CareDefinitions
Adulterated specimen: A urine specimen containing a substance that is not a normal constituent or containing an endogenous substance at a concentration that is not a normal physiological concentration.
Diluted specimen: A urine specimen with creatinine and specific gravity values that are lower than expected for human urine. 2017-00979.pdf (govinfo.gov)
Substituted specimen: A urine specimen with creatinine and specific gravity values that are so diminished or so divergent that they are not consistent with normal human urine. 07-4428.pdf (govinfo.gov)
Creatinine is endogenously produced and cleared from the body by the kidneys. It is a normal constituent in urine. Normal human urine creatinine concentrations are at or above 20 mg/dL.
pH is the measurement of acid-base. Human urine is usually near neutral (pH 7), although some biomedical conditions affect urine pH. HHS set the program cutoffs for pH based on a physiological range of approximately 4.5 to 9
Specific Gravity is a measure of the density of a substance compared to the density of water. For urine, the specific gravity is a measure of the concentration of dissolved particles in the urine. Normal values for the specific gravity of human urine range from approximately 1.001 to approximately 1.020.